This can help you see where the foot cannot take stress Above Right Front FootVideo Club Foot in Horses In this excerpt from the November 18 episode of Ask the Vet, Dr Gray and SmartPaker Dan turn to Danvers Child, the SmartPak Hoof Health Consultant, for assistance with a question on a horse with a club foot to clear up some confusion around the topicThe most frequently recognized form of clubfoot in horses occurs in sucklings or weanlings at approximately 2 to 8 months of age1–3,6–8 It is commonly a unilateral condition but occasionally affects both limbs The first clinical sign recognized is an upright appearance of the foot combined with the inability of the heels to contact the ground

Flexural Deformities In Horses Musculoskeletal System Merck Veterinary Manual
Club foot horse pictures
Club foot horse pictures- Clubfoot describes a range of foot abnormalities usually present at birth (congenital) in which your baby's foot is twisted out of shape or position In clubfoot, the tissues connecting the muscles to the bone (tendons) are shorter than usual Clubfoot is a fairly common birth defect and is usually an isolated problem for an otherwise healthyExplore Kayla Reynolds's board "Club Foot" on See more ideas about club foot, horse health, horse care



Club Foot In Horses Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment Recovery Management Cost
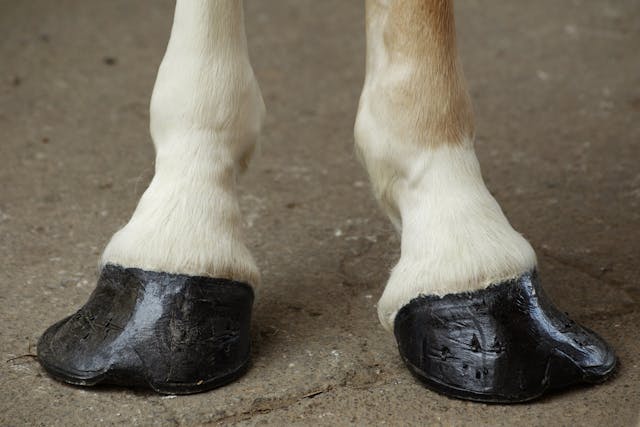
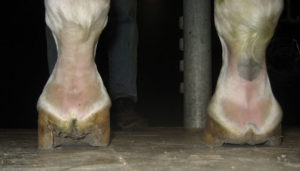
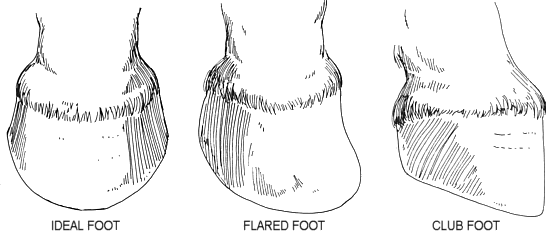
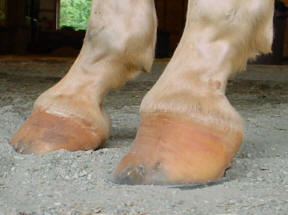
Telltale signs of a club foot may include an excessively steep hoof angle, a distended coronary band, growth rings that are wider at the heels, contracted heels, and dished toes Most horses only have one club foot, but it is possible to have multiple Club feet can be congenital, or they can develop later in lifeHorse with club foot has one hoof that grows more upright than the other The "up" foot is accompanied by a broken forward pastern, that is, the hoof is steeper than the pastern (Photo 1) In a normal foot, the hoof capsule and the pastern align Radiographs will show that the boney column itself is misaligned, with permanent rotation of the coffin joint (Photos 2 and 3)FIGURE 1 An excellent example of mismatched feet
In a club foot, the angle of the hoof and pastern in relation to the ground is abnormally steep In the past, the condition was defined as any hoof angle that exceeded 60 degrees, but the reality is not quite that exact A "normal" angle for a horse's Things to look for to determine if your horse has a club foot Clue #1 The flare is at the toe, not on the sides Clue #2 After rasping down the outside of the hoof at the toe, use a hoof protractor to measure the angle of the hoof An angle of more than 60 degrees indicates a possible club foot Clue #3Causes of Club Foot in Horses The deep flexor tendon is shorter than the bones causing a pulling on the coffin bone in the hoof which causes a deformity in the shape of the hoof Congenital deformity at birth (occurring within the mare's uterus) likely due to multiple factors
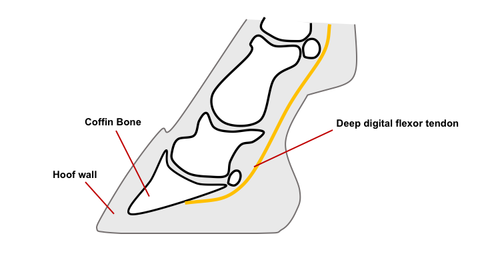
George Lane, better known as Clubfoot George, was an alleged outlaw who was hanged on in Virginia City, MontanaLane was later alleged to have been a member of a criminal gang known as the Gang of Innocents and sentenced to death The execution was carried out by the Montana Vigilantes, a committee which functioned during Montana's gold rush in 1863 and 1864A club foot results from a flexural deformity of the distal interphalangeal joint that is characterized by a shortening of the deep digital flexor tendon musculotendinous unit Flexural deformities are a problem not only in foals but are also responsible for the club foot conformation seen in adult horsesWith the club footed horse, the first thing to understand is that the horse has a deformity and as such it is always going to need a high degree of hoof maintenance, for the term of its natural life To identify the club foot we must know what is considered 'normal' and then compare the difference




The Barefoot Horse Magazine What S The Problem With A Club Foot Can You Or Should You Try Fix A Club Foot By Trimming Shoeing Can A Horse With A Club
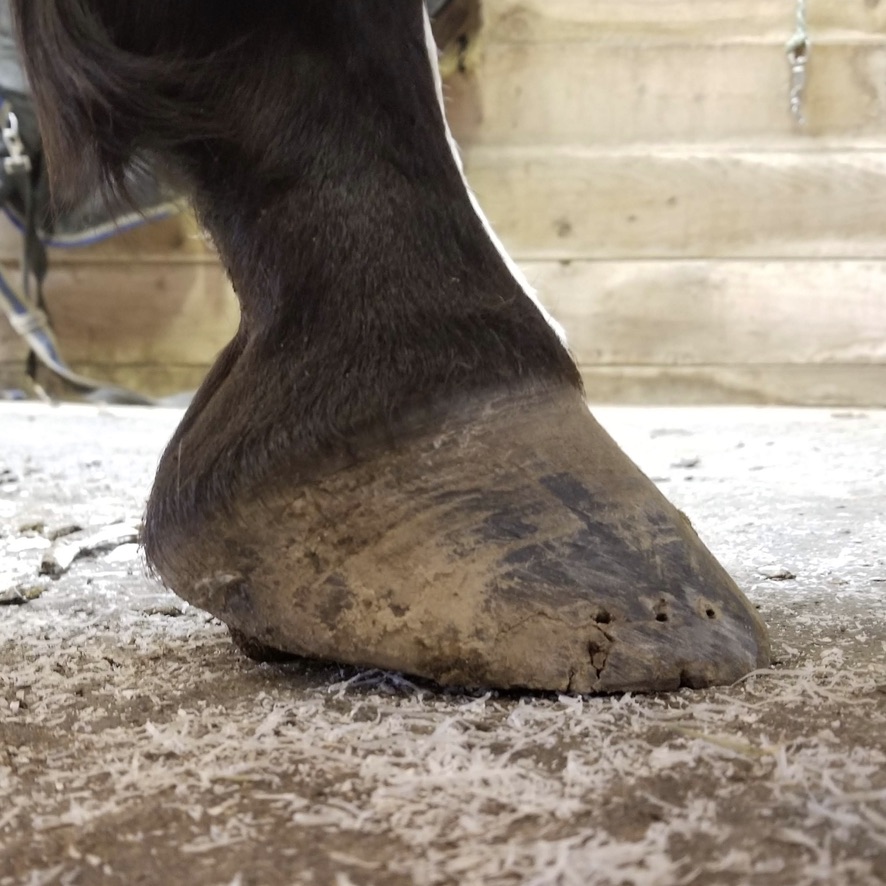




Low Foot Case Study Dixie S Farrier Service
When asked to work on a horse with a club foot, take extra time to evaluate the whole horse Look at the horse from all angles Watch the horse as it takes a couple of steps;Club foot refers to a tendon flaw that causes the hoof to be very upright Often, club foot affects both front legs with one being more severe than the other Club foot can occur before or after birth in foals After birth foals acquire club feet when the bones grow faster than the tendons Many articles have been written about club 'footed' horses Actually, horse do not have 'feet', dogs and humans do, but horses have hooves Therefore the term 'barefoot', as much as it is in common use now, really is a misnomer When we ride without hoof protection, we ride 'bare hoof' Ah well, a pet peeve




Understanding Club Foot The Horse Owner S Resource



1
Club foot refers to a hoof that is more upright than normal It is often associated with a concave front (dorsal) hoof wall, high (often contracted) heels, and widening of the white line from mechanical stretching of the hoof wall attachments (the laminae) Adult club foot requires a completely different approach to treatment than juvenile club foot148 of 180 results for "clubfoot shoes" Price and other details may vary based on product size and color 14 ikiki Squeaky Shoes for Toddlers with On/Off Squeaker Switch 47 out of 5 stars 8,0 $3295 $ 32 95 FREE Shipping by Amazon Memo Honos Orthopedic Corrective Ankle Brace Sandal 46 out of 5 stars 29Club foot refers to a tendon flaw that causes the hoof to be very upright Often, club foot affects both front legs with one being more severe than the other Club foot can occur before or after birth in foals After birth foals acquire club feet when the bones grow faster than the tendons




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals




Club Foot Ronaldmarshall
"Clubfoot" George Lane, a shoemaker by trade, was accused of being a member of Henry Plummer's gang of Innocents and hanged by Montana Vigilantes in January 1864 A small man who was crippled due to a birth defect, Lane was originally from Massachusetts and made his way to the west during the California Gold Rush He first worked on a farm in Yuba County, before makingClub Foot in Horses Brian S Burks DVM, Dipl ABVP BoardCertified in Equine Practice Horses often have slightly asymmetrical feet, but they should not differ drastically A clubfoot, or a distal interphalangeal (coffin joint) flexural deformity, may affect the horse at any stage of life from neonate through adulthood A few days later, the dealer delivered the horse to me The mare was heavily sweating when she got out of the trailer Her upright hoof had broken off, revealing a club foot, and she was lame We proceeded to pull the shoes asap to transition her to barefoot We also fitted her with Old Macs G2, which made her comfortable and forward going




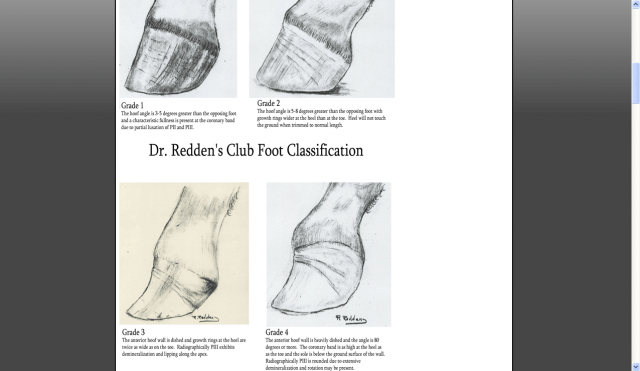
Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome




Understanding Club Foot The Horse Owner S Resource
The horse walks on its toes or knuckles in the fetlocks or occasionally the pastern joint Nutritional errors referable to problems associated with bone growth (ie, osteochondrosis and physitis) are intimately associated with the syndrome and must be addressed as part of treatment The term "clubfoot" gets thrown around a lot when describing the way a horse, particularly a sale prospect, looks But what does the term mean, and what actually constitutes a clubfoot on a horse? With respect to the club foot, the heel of the affected foot grows faster and the hoof more upright in appearance due to most of the horse's weight being placed on the opposite foot This can be due to either pain or a preference of "feeding posture" which they determine early on in




What Is A Club Hoof Versatile Horsemanship Youtube
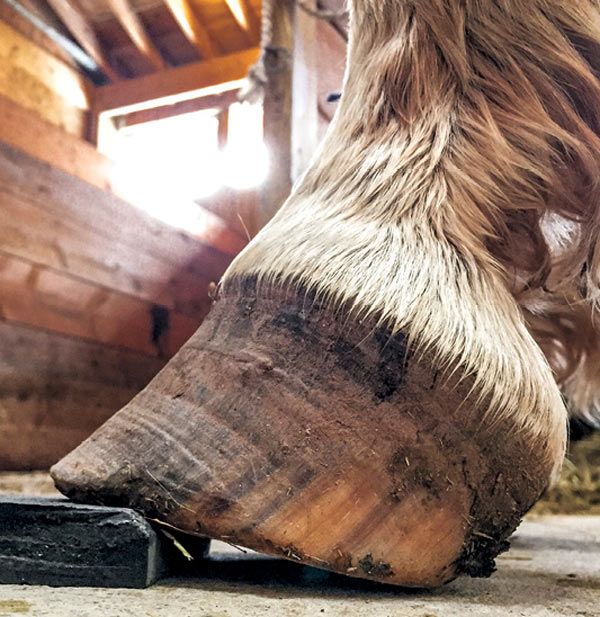




Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles American Farriers Journal
Pictured Above A club foot is a morphological change in the hoof that's due to a shortening of the musculoskeletal tendinous unit of the deep digital flexor tendon, says Vern Dryden, an equine veterinarian and farrier The contraction creates a downward pull on the third phalanx Photo Vern Dryden It's not uncommon to observe minor asymmetries in any horse's feetWritten and presented April 12 by RF (Ric) Redden, DVM To better understand the club foot syndrome, we must be familiar with the mechanical formula and how it greatly influences the various degrees of hoof capsule distortion and bone remodeling associated with this syndrome There appears to be a direct relationship between the degree of tension increase or contributiveClub Foot By Dr Lydia Gray, SmartPak Medical Director/Staff Veterinarian What is it?




Club Foot Results In A Vertical Hoof Wall Compared To Other Feet A Dropped Sole And A Dished Front Dorsal Hoof Wall It Res Club Foot Horse Health Hoof Care



Boarding At Yucca Veterinary Medical Center
Socalled "clubfoot" has long been a vexing problem for horsemen, veterinarians, and farriers The term clubfoot is a misnomer for the condition in the horse and correctly refers only to a congenital anomaly of the human foot Lungwitz (1910) properly defined and described the condition for the horse There are three forms 1 Stumpy hoofThe equine club foot is defined as a hoof angle greater than 60 degrees What we see externally as the equine clubbed foot is actually caused by a flexural deformity of the distal interphalangeal joint (coffin joint) Causes include nutritional issues, heredity, position in the uterus or injury Most horsemen define a club foot as hoof and pastern angle of more than 60 degrees, making the foot more upright than normal The affected hoof is usually stumpy with a short toe and long, upright heel



Understanding Club Foot Pressreader




How D That Happen Origins And Remedies For Clubfoot Horse Racing News Paulick Report
Club foot refers to a tendon flaw that causes the hoof to be very upright Often, club foot affects both front legs with one being more severe than the other Club foot can occur before or after birth in foals After birth foals acquire club feet when the bones grow faster than the tendonsSponsored By Equilox Bob Smith, the head instructor of the Pacific Coast Horseshoeing School, discusses the grades of club feet and the strategy needed to a Horses often possess mismatched feet, and this asymmetry can sometimes be traced to clubfoot The mechanical cause of clubfoot involves hyperflexion of the distal interphalangeal joint, the articulation between the short pastern bone and the coffin bone, due to shortening of the deep digital flexor tendon




Hoof Conformation Vs Horse Conformation Scoot Boots Us Retail




Flexural Deformities In Horses Musculoskeletal System Merck Veterinary Manual
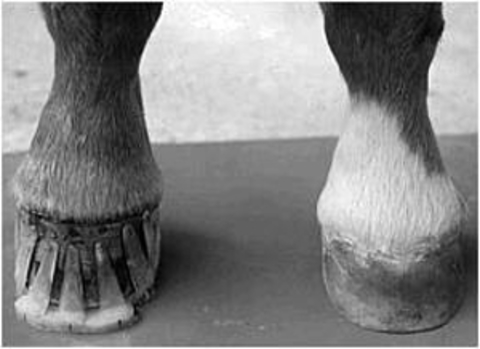
A "clubfooted" horse is defined by most people as a horse with one hoof that grows more upright (particularly at the heel angle) than its mate on the otherA club foot is a DEFORMITY and for any horse to win at top level competition it needs every possible advantage and no drawbacks The only way to stop continuing problems with club footed horses is not to breed from them After 11 months of gestation, it is a costly and heart breaking exercise if it results in a club footed foalUnlike other farm animals, the horse is serviceable only when in motionAny abnormal deviation in the structure or action of a horse can render it partly or completely useless Therefore, any defect that affects serviceability is considered an unsoundness, ie, lameness, blindness, faulty wind, etcThose defects that detract from appearance but do not impair serviceability are considered



Shoeing News Club Grades Harness Racing Newsroom Usta Ustrotting




The Importance Of Physical Maturity In The Horse Horsetalk Co Nz
3 Juvenile Presentation The most frequently recognized form of clubfoot in horses occurs in sucklings or weanlings at approximately 2 to 8 months of age 13,68 It is commonly a unilateral condition but occasionally affects both limbs The first clinical sign recognized is an upright appearance of the foot combined with the inability of the heels to contact the groundThe xray will show whether the hoof pastern axis is parallel If the axis is broken forward (club foot) or if the axis is broken back (long toe underrun heel), the radiograph will reveal the degree of deformity and the best way to trim the foot to improve it Using landmarks, measurements can be drawn on the radiographs and transferred to the Club foot is horseman's term for contraction of the deep digital flexor tendon (DDFT) The foot will have a steeper angle and smaller size than it's mate The most accepted causation is that horses with long legs and/or short neck adopt a grazing stance where one leg is constantly stretched while the other is not



Lesson 4
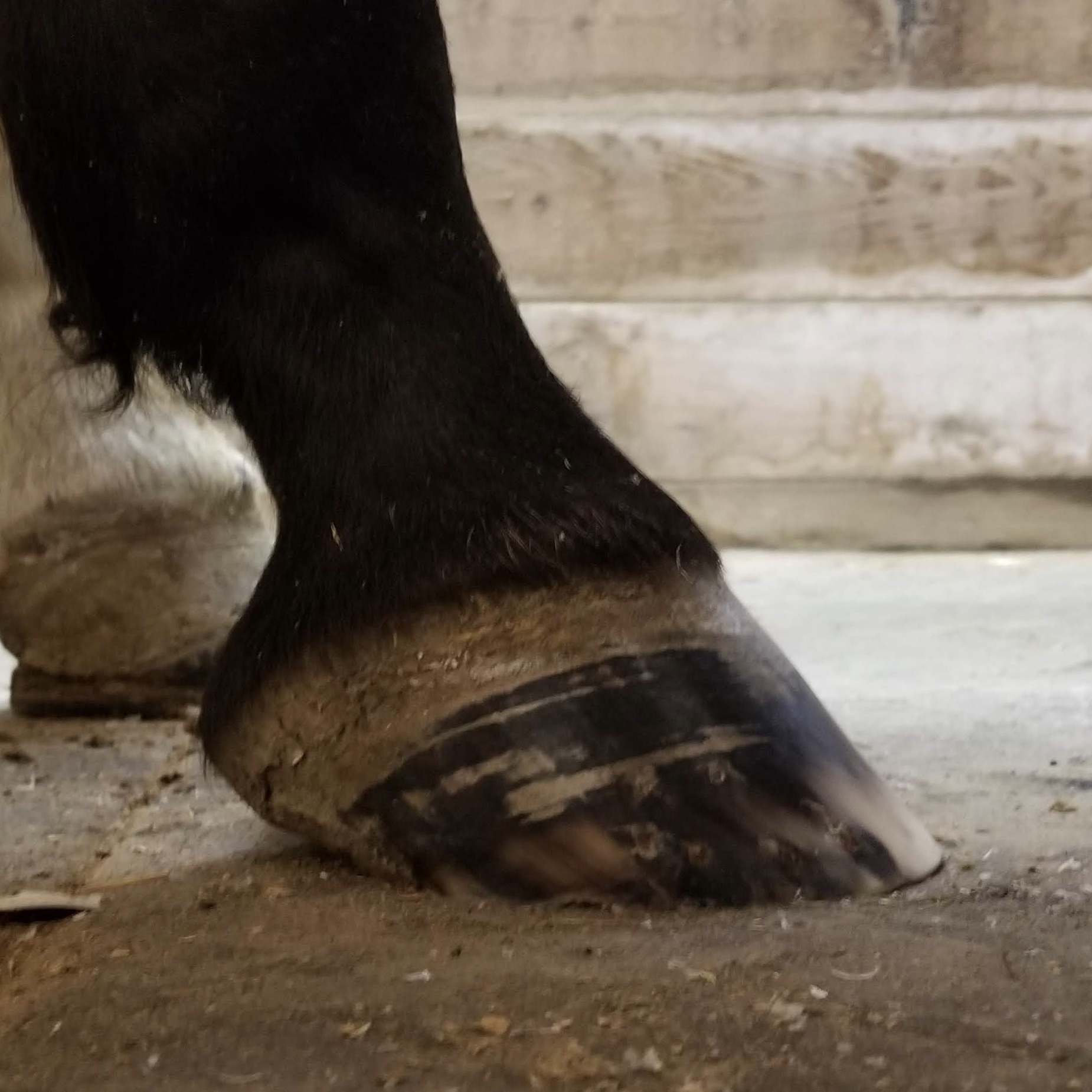




Low Foot Case Study Dixie S Farrier Service
Club foot 1 CLUB FOOT Presented By Sushant 2 INTRODUCTION Talipes Latin talus (ankle) pes (foot) Equino indicates the heel is elevated (like a horse's) varus indicates it is turned inward It is a congenital malformation of the lower extremity that affects the lower leg, ankle, and foot Club foot, also called congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV), isExplore LISA's board "equine clubfoot" on See more ideas about horse health, equines, horse care tipsThe classic club foot is easy to spot – upright hooves, long heels, pronounced coronary band, dished hoof wall, contracted appearance It's not pretty, and it's definitely less functional than a normal hoof, but with proper management techniques, club foot doesn't have to spell the end of a horse's athletic life




Pdf Management Of Clubfoot In Horses Foals To Adults Semantic Scholar




Natural Angle Volume 15 Issue 1 Spanish Lake Blacksmith
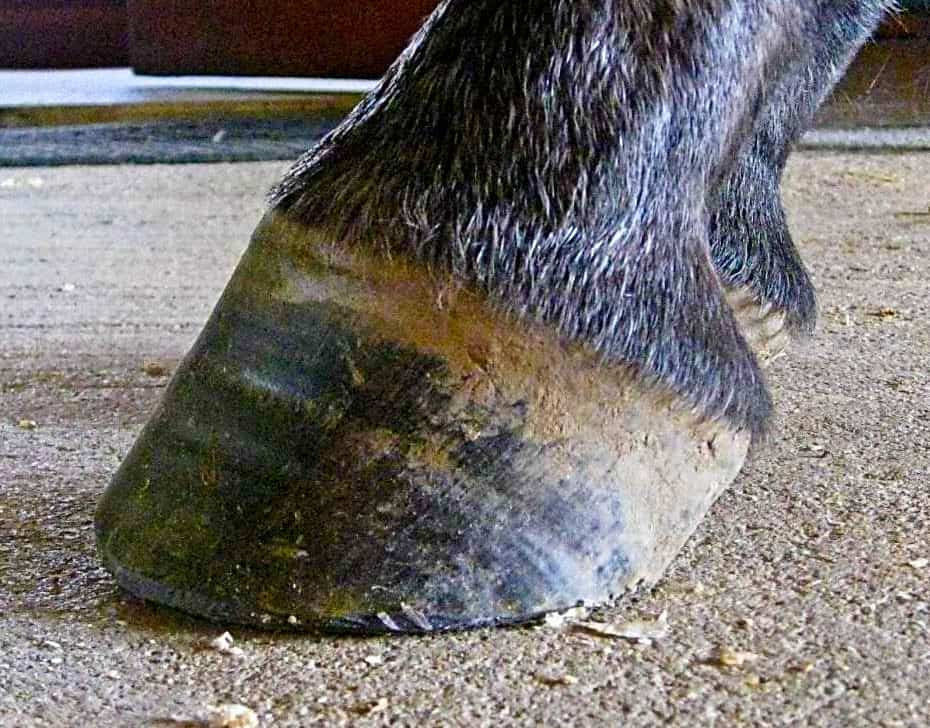
A horse with a club foot is kind of like a horse in high heels The hoof angle becomes raised and the horse walks on his toe due to a shortening ofClub foot is defined as a flexural deformity of the coffin joint and is a common problem in young, growing horses Characteristics of a club foot are a prominent or bulging coronary band, a very upright hoof wall angle, a heel that doesn't touch the ground, a dish in the hoof wall at the toe, growth rings A club foot horse is typically recognized and defined as having one front hoof growing at a much steeper angle than the other, with a short dished toe, very high heels, extremely curved wall and straight bars The club foot is also generally much narrower than the other and will usually have a substantially smaller and sensitive frog



Club Foot In Horses Equine Chronicle



Clubfoot 5 Yo Morgan Mare Barefoot Hoofcare
One of the most common hoof deformities, which develops as a result of a change in the healthy balance and biomechanics in the horse's foot, is the club foot What Is Club Foot? A club foot alters a horse's hoof biomechanics, frequently leading to secondary lamenesses Affected horses tend to land toefirst, and their heel's growth rate isThis "compensation" type of club foot has a strong heel structure with upright, flat bars the heel looks like a fortress The sole thickens in the heel to a level that works for the horse This kind of club foot should be respected for the job it's doing for the horse




News Feed Casey Son Horseshoeing School




Webinar Shoeing The Club Footed Horse Youtube
In this excerpt from the November 18 episode of Ask the Vet (https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=BfXotLp1), Dr Gray and SmartPaker



Www Theneaep Com S Xia1nkm5hdp7yhwyucxfn39k42qa8m



Club Feet In Foals
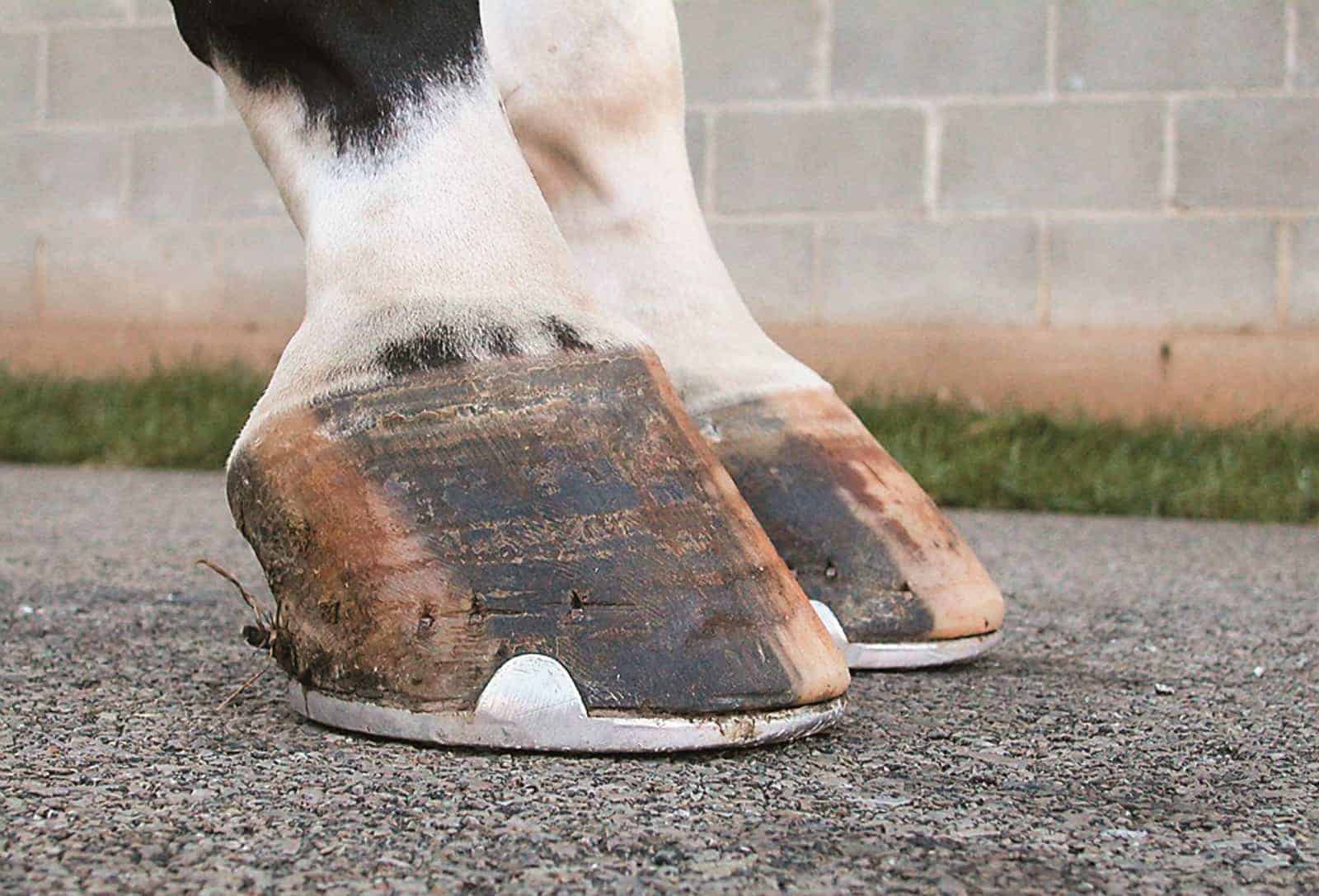




Managing The Club Foot The Horse




Ballerina Syndrome Where The Heels Remain Off The Ground Even At The Download Scientific Diagram
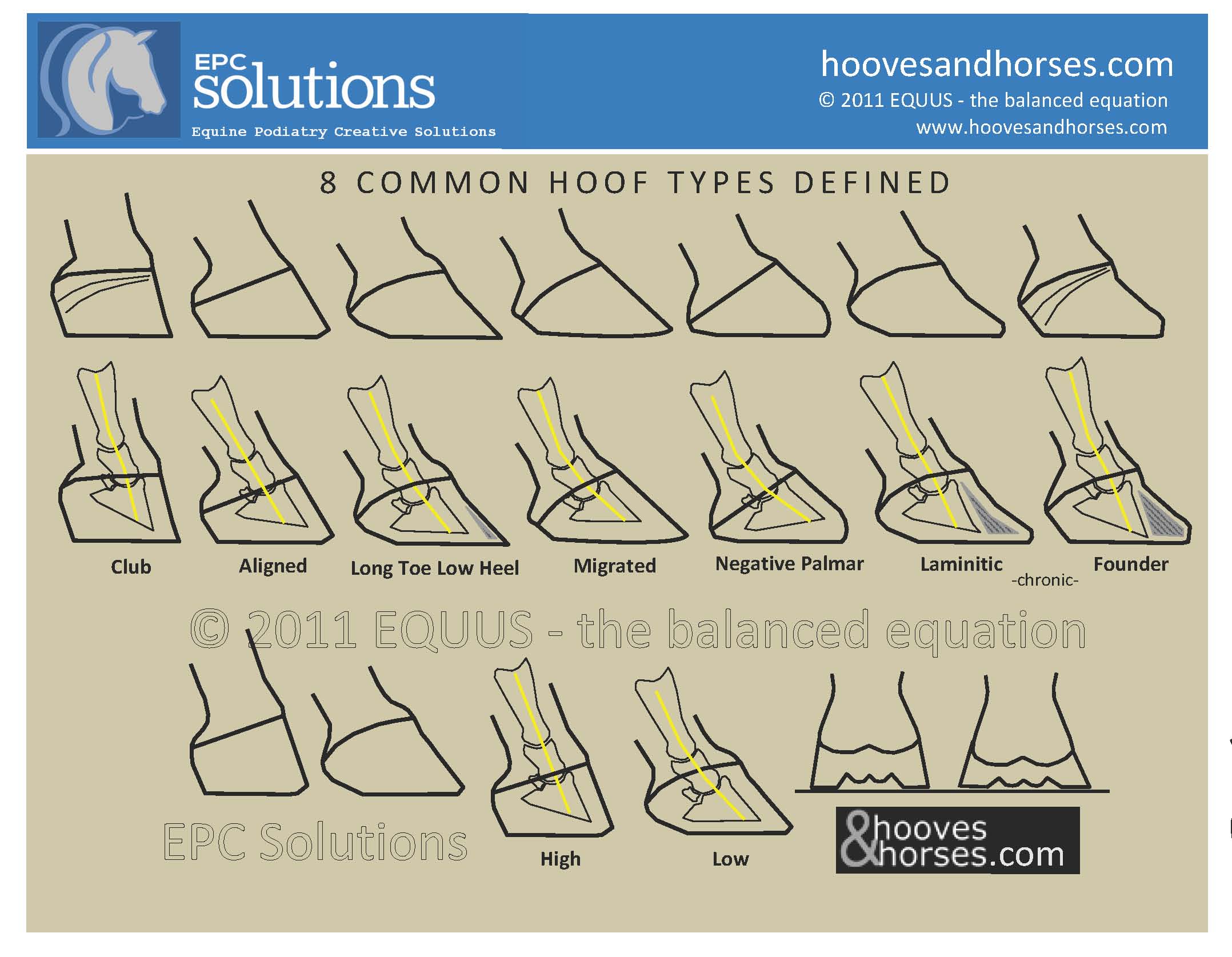



8 Hoof Types Explained




Equine Therapeutic Farriery Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles




Why Some Horses Develop A Clubbed Foot Holistichorse Com



ep Org Sites Default Files Issues Proceedings 12proceedings In Depth The Foot From Every Angle Hunt Pdf



Farriervet Lancaster Club Foot



Horse Hoof Irregularities Club Foot Integrity Horse Feed




Club Foot In Horses The Horse S Advocate




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Club Foot



So Called Club Foot By James R Rooney Dmv




Portfolio Barefoot Trimming



Basic Shoeing Working With A Club Foot Farrier Product Distribution Blog




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Managing The Club Hoof Easycare Hoof Boot News




Hoof Conformation Vs Horse Conformation Scoot Boots Us Retail



Club Feet The Brutal Truth David Farmilo




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Equine Podiatry Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles



Would You Buy A Horse With Club Foot Pics The Horse Forum



1



Would You Buy A Horse With Club Foot Pics The Horse Forum



Ppt 5 Most Common Hoof Pathologies Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Contact Us Palmetto Equine Veterinary Services



Www Theneaep Com S Xia1nkm5hdp7yhwyucxfn39k42qa8m




Clubfoot Or Club Foot Or Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Ctev Equine Before And After The Operation Vintage Engraved Illustration Usual Medicine Dictionary By Dr Labarthe 15 Canvas Print Barewalls Posters Prints Bwc




Michael Porter Equine Veterinarian 12



Managing The Club Hoof Easycare Hoof Boot News
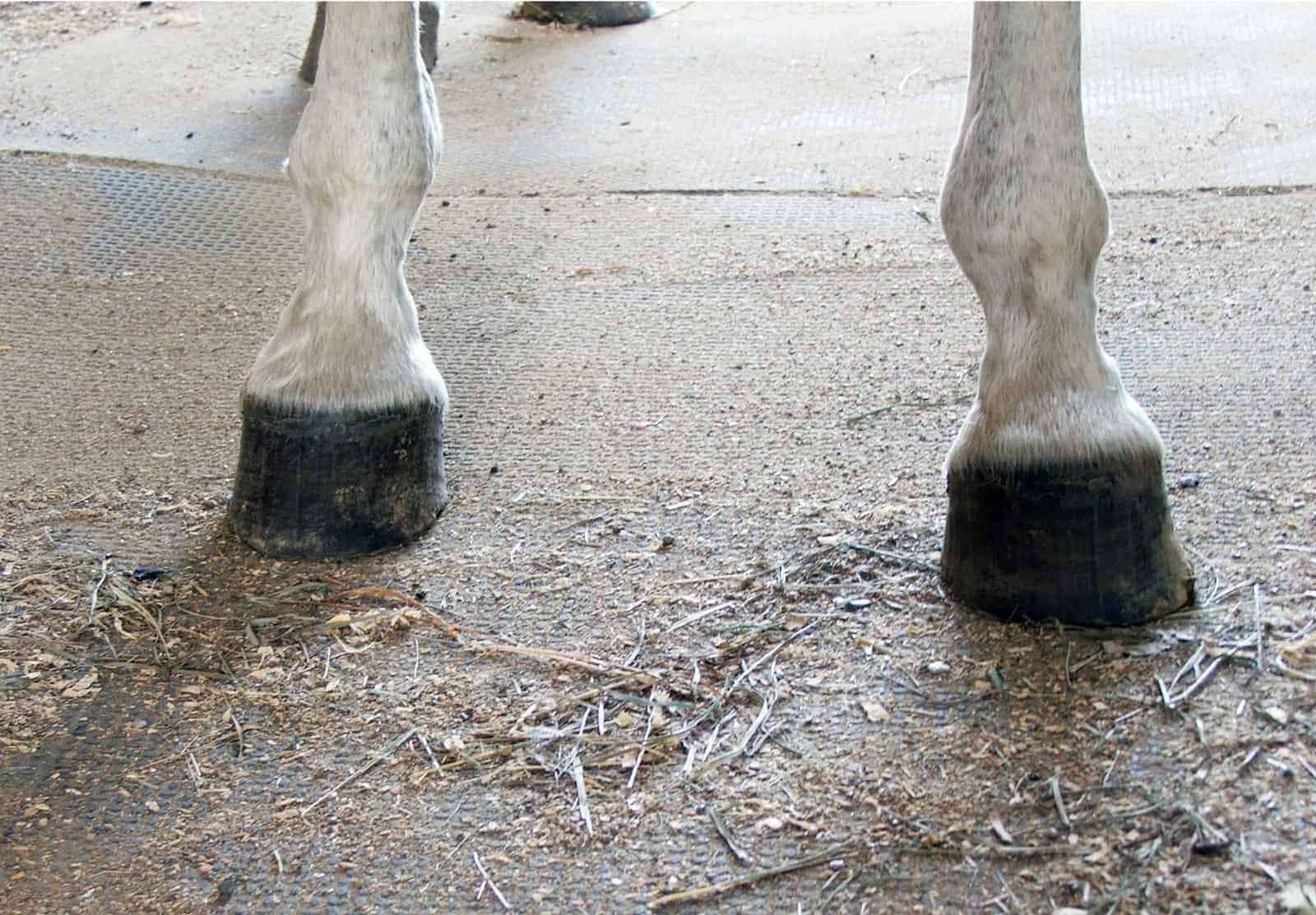




Club Foot Heritability In Horses The Horse



Farriervet Lancaster Club Foot



Animal Mrt Effect Of Hoof Distortion On Muscoskeletal Issues




Club Foot Just How Sore Is Your Horse Casey Son Horseshoeing School




Mobile Equine Diagnostics Inc Posts Facebook




Frequent Trips Aid Club Foot American Farriers Journal




The Club Foot Is It No Big Deal Or A Deal Breaker




Natural Angle Volume 15 Issue 1 Spanish Lake Blacksmith



Club Feet In Foals



The Tolerable Club Foot The Horse



Club Foot
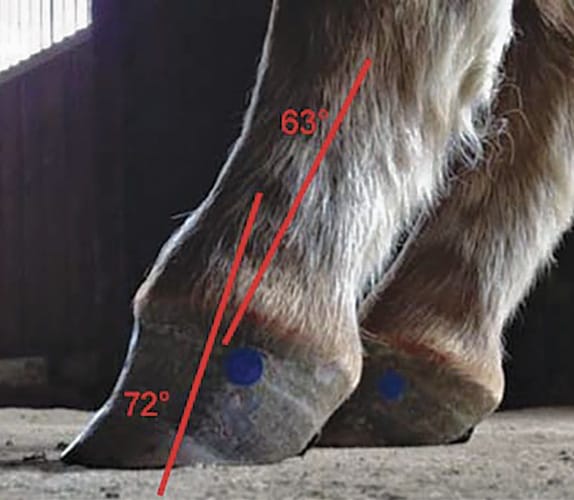



Defining And Fixing A Horse S Club Foot American Farriers Journal



Club Foot



Club Foot In Horses
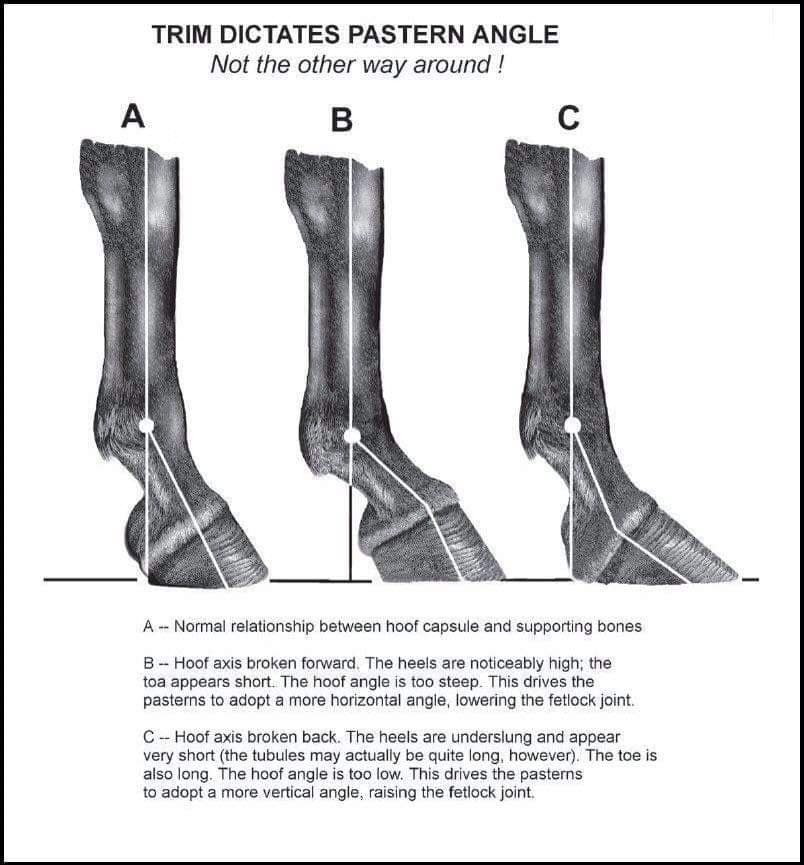



What Your Horse S Hoof Angle May Be Telling You Horses



Performanceequinevs Com Wp Content Uploads 19 12 Equine Foot Secrets Ebook Compressed Pdf



Q Tbn And9gct650ae6d8vnmqnvcvl4zcvlmqyfuvklxwislafu3ckq06siyee Usqp Cau



Welcome Princess 17 Page 2 Zenyatta Com Forums




Club Foot What Does The Future Hold For Your Foal H H Vip Horse Hound
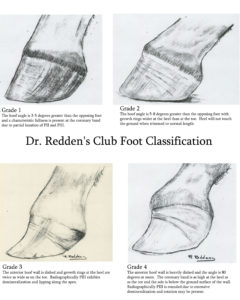



Horse Hoof Irregularities Club Foot Integrity Horse Feed



Q Tbn And9gcsfmoxca22quhhmkpddabgxcxz70dgjb50dvfe9hvos1glprvjn Usqp Cau




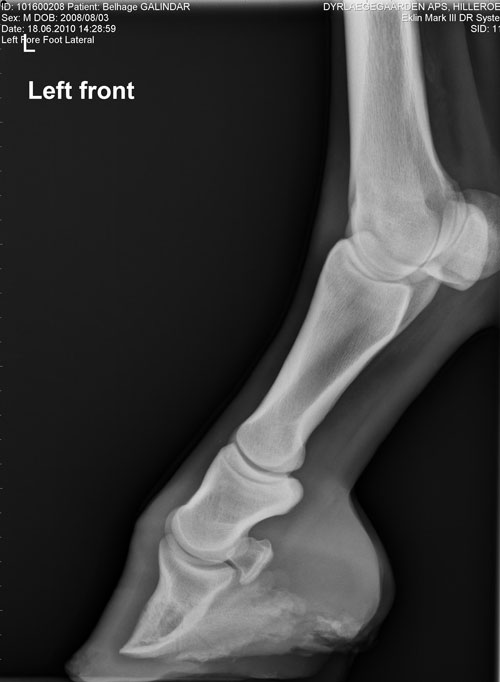
Equine Club Foot




Pdf The Incidence Of Acquired Flexural Deformity And Unilateral Club Foot Uneven Feet In Thoroughbred Foals



Club Foot In Horses Equine Chronicle



Club Feet Springhill Equine Veterinary Clinic



Club Foot



Is This A Club Foot Horsetalk Co Nz
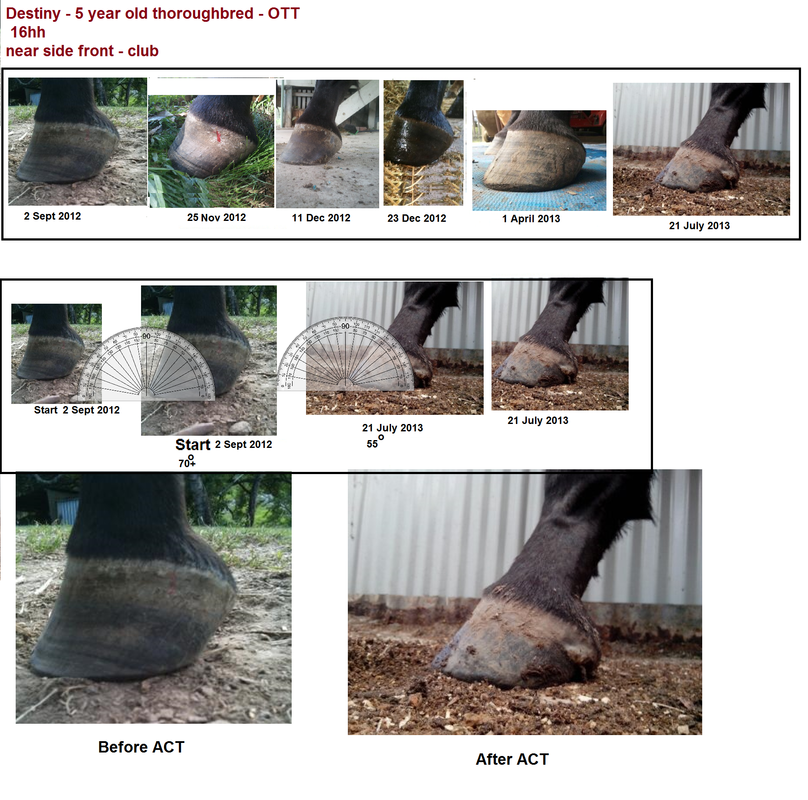



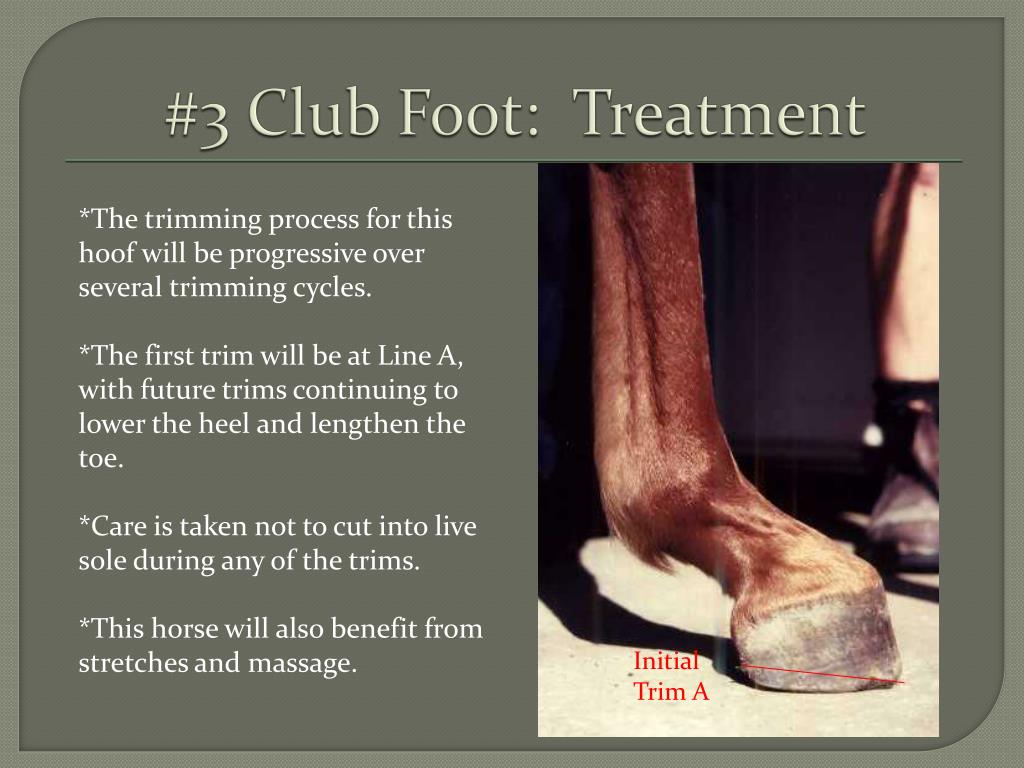
Club Foot Rehabilitation Act Trimming Strategy




Defining And Fixing A Horse S Club Foot American Farriers Journal




Shoeing Options For Club Foot In Horses



ep Org Sites Default Files Issues Proceedings 12proceedings In Depth The Foot From Every Angle Hunt Pdf



Club Foot




Clubfoot Equine Before And After The Operation Vintage Engravin Stock Vector Illustration Of Ancient Finger




Shoeing Options For Club Foot In Horses
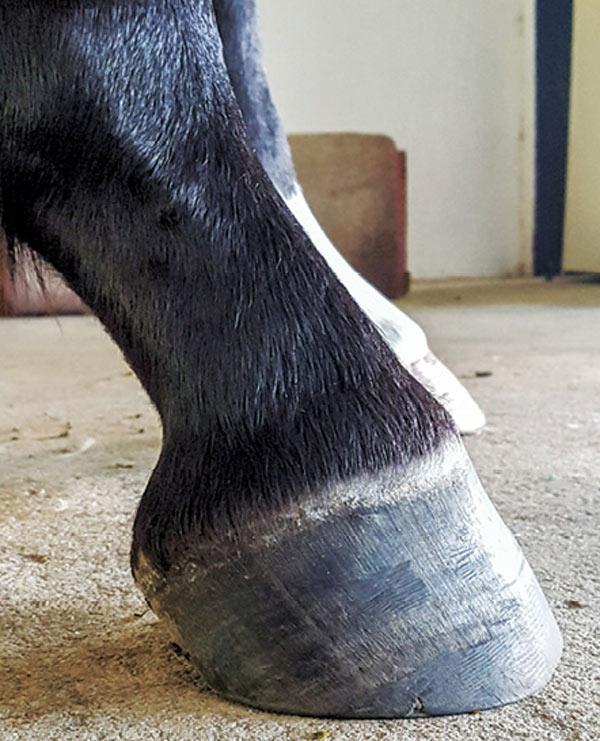



Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles American Farriers Journal




Club Foot In Horses Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment Recovery Management Cost




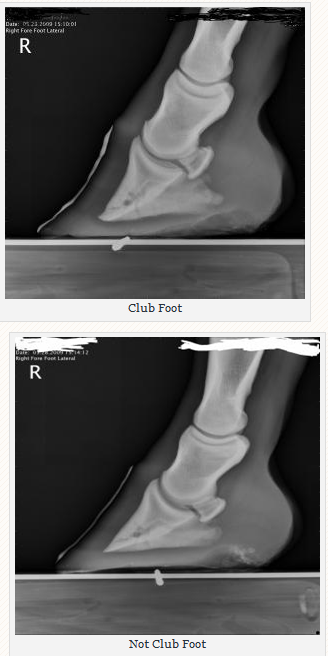
Club Foot Or Not Barefoot Hoofcare



Basic Shoeing Working With A Club Foot Farrier Product Distribution Blog
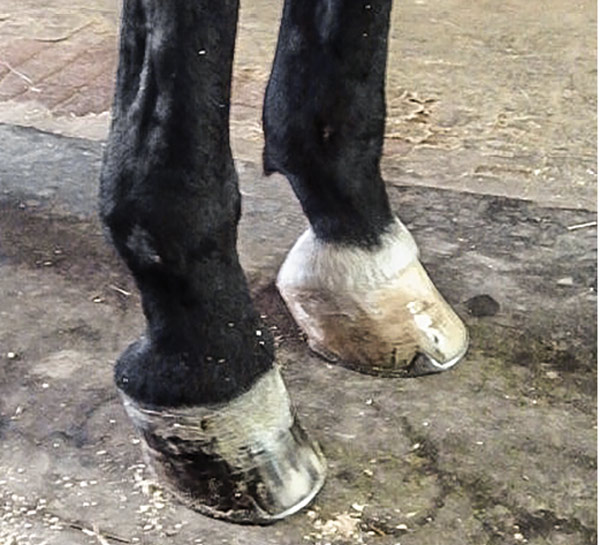



What Advice Has Been Most Helpful When You First Encounter A Club Foot American Farriers Journal
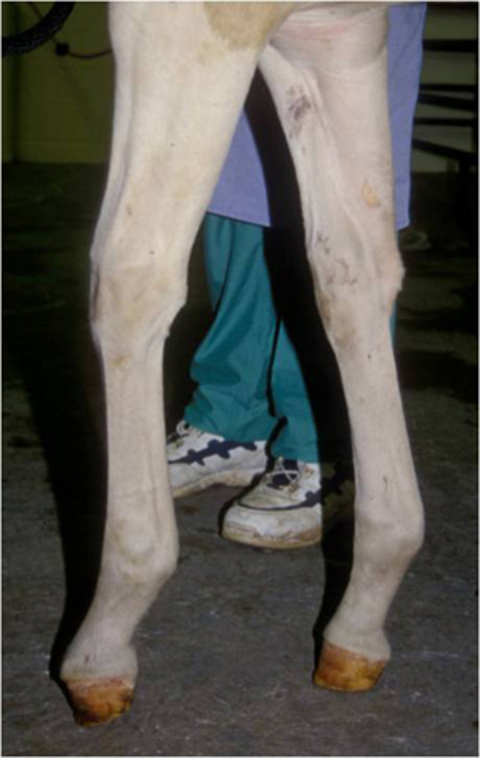



Club Feet In Foals



Basic Shoeing Working With A Club Foot Farrier Product Distribution Blog




Equine Club Foot




Club Foot In Horses The Horse S Advocate




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals




Club Foot In Horses Brian S Burks Fox Run Equine Center Facebook



Club Feet The Brutal Truth David Farmilo



Club Feet The Brutal Truth David Farmilo



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿